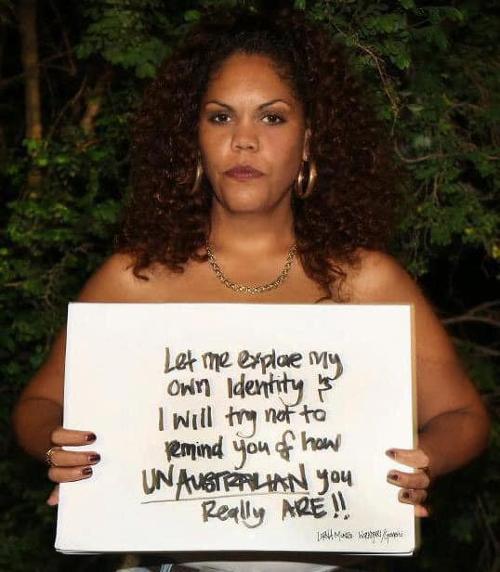Search
You searched for contributors, issues and articles tagged with Indigenous ...
Contributors
Issues






















Articles

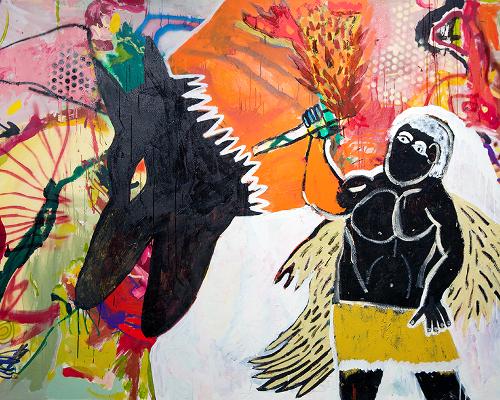
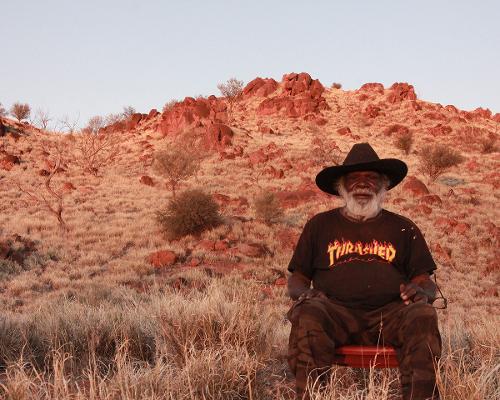
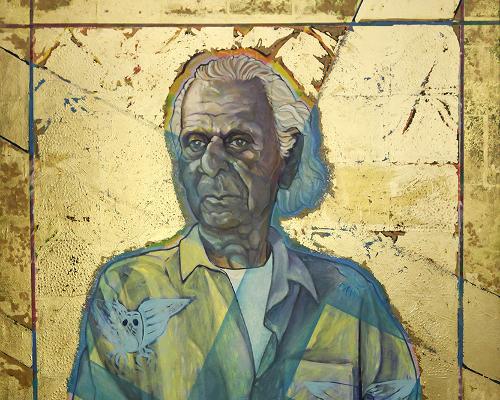
In the rapidly expanding literature on the Tennant Creek Brio, writers have touched upon a decidedly ‘masculine’ quality in the group’s work. John McDonald calls the Brio’s work ‘incredibly aggressive’ and ‘raw’ and ‘wild.’ Erica Izett, the Brio’s regular curator and greatest advocate, refers to their work as a form of insurgent ‘guerrilla theatre.’ These masculinist tendencies should be of little surprise. The Brio started in 2016 as an art therapy group as part of Strong Men, Strong Families through funding from the Anyinginyi Health Aboriginal Corporation facilitated by painter Rupert Betheras. It grew to have about twenty men involved before moving to the Nyinkka Nyunyu Art and Culture Centre in 2017, where it was declared an artist collective.

My formal arts education began in a strange place: the Elisabeth Murdoch building at the University of Melbourne where I took an art history elective. Built in 1885 by Joseph Reed, the Gothic architecture reinforced the rigid authority of the colony. Glaringly elitist, it resembled both church and orphanage. It was full of confusing hallways, which remained impossible to navigate. Inside its constructed edifice, middle-aged white men in paisley shirts lectured, with exotic hand gestures, on First Nation artists (when they were spoken of at all). And white women in the faculty asserted a self-righteous paternalism that was far worse.
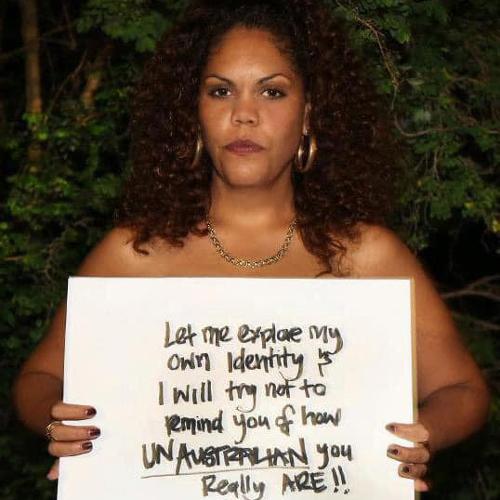
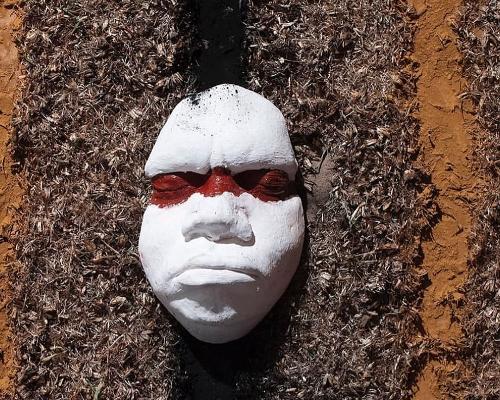
I paint my face as my mother’s mothers have done before me
In this new ritual sitting on my bedroom floor
We name each pigment after revolutionaries
Because I am my mother’s daughter

An interview with First Nations curators Kathleen Ash-Milby, Maia Nuku and Nigel Borell.

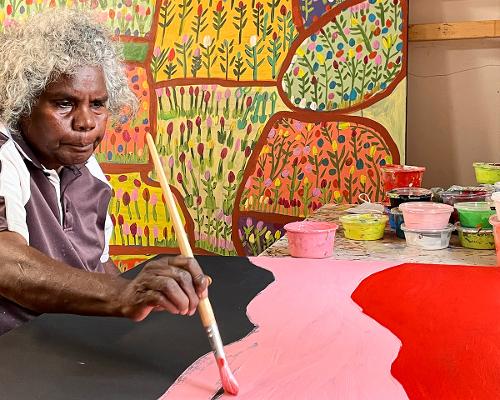
I am of the Tati Tati, Latji Latji, Wadi Wadi, Mutti Mutti, Yitha Yitha and Nari Nari peoples of the Murray River, Murrumbidgee River, Lachlan River, Edwards River and Wakool River Country in Australia.
I continue to practice and share my Ancestral peoples connection to Mother Earth through my art, songs, dance, language, cultural heritage, customs, beliefs, spirituality and knowledges. I care for Country and my people and I will remain on Country forever, just as my Ancestral people always have since creation.

In 2019 I composed a poster form multilingual guide in Sāmoan, French and English called Punāʻoa o ʻupu mai ʻo atumotu/Glossaire des archipels to represent currents of thought and action in international Indigenous visual cultures. I worked with my friend, celebrated Nêhiyâw typographer and graphic designer Sébastien Aubin, to render my learnings from a constellation of mentors, knowledge keepers and sources during my doctoral research into international Indigenous curatorial practice into a poster form multilingual guide. The work draws on extensive discussions, residencies, exhibitions, gatherings throughout 2015–18 across the Great Ocean from north‑eastern North America to south‑eastern Australia.

kʔimitʸɨ, we are far away.
tsʔiqɨʔ, the tides are low.
qšimuʔ, like many words in tɨnɨsmuʔ tiłhinktitʸu, explains a story rather than a fixed or singular vocabulary. Olivella biplicata has a gorgeous shell, with colours that smoothly transition from stark white to milky lavender to rich honey golds, in combination or alone, along a softly curving spire. A being reflecting spiritual wealth and a symbol of exchange from our homelands spanning mountain ranges east to nitspu nakota ktitʸu, south well beyond recently imagined lines of occupying nations, and along margins of the sea north to nitspu unangan ktitʸu, qšimuʔ grounds yak titʸu titʸu yak tiłhini in a vast network of relation. yakʔitɨnɨsmuʔ wa yakʔitotomol, which echo the cadence, vocabulary, and sewn-planks of many other nations, extend these connections well across łpasini, the one ocean.

On a night in the woods north of Tallahassee at Pine Arbor Tribal Community, Mvskoke scholar, linguist and elder Sakim told me that in Muscogee (Creek) cosmology, what we know of as the Milky Way is the path of ancestors—and he said, “I think we all know, our bodies are stars.” And the belt of Orion? It isn’t a belt. And it isn’t Orion. It’s a butterfly. And the belt part is actually the juicy middle part of the butterfly. And the top wing is this world and the bottom wing is a reflection of this world. And then there’s that liminal, juicy line. So there’s always you, and there’s always the reflection of you, in play.
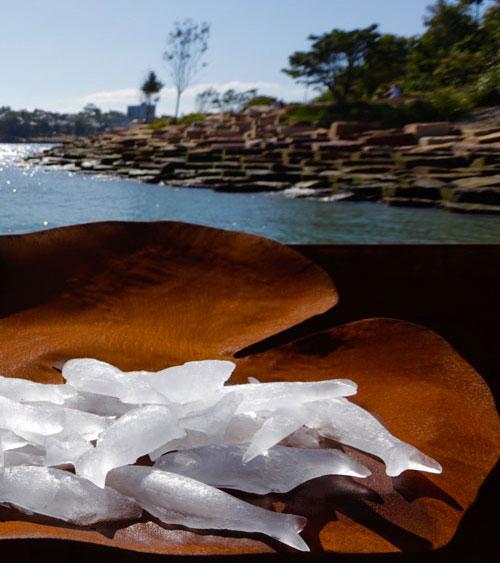

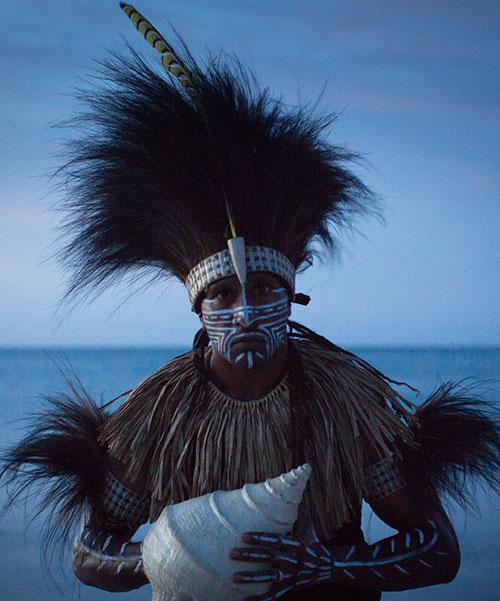
As people walk down that little wharf towards the canoe, I hope they remember how it was back in the day and how our old ancestors used to live and survive. And I want them to think back and imagine if they can, the women out in the canoes, and what it would have looked like and how beautiful it would have looked like with the fires going and we must not forget them, our ancestors. They were some special people. Because all the thousands of years they lived here says it all. It just says it all, how powerful and strong they were. And survivors… still survivors today.
Phyllis Stewart

A couple of years ago I quipped to my friend Alec Coles, who had recently taken up the position of CEO at the West Australian Museum, that the spirit of terra nullius lurks beneath the floorboards of every museum and art gallery in Australia. Apparently, he has dined out on this slightly parsimonious comment once or twice since. Alec likes to raise the stakes in discussions with his colleagues about the responsibilities that history demands of them as leaders of major collecting institutions—each with its own problematic legacy in terms of respecting and representing Indigenous culture.

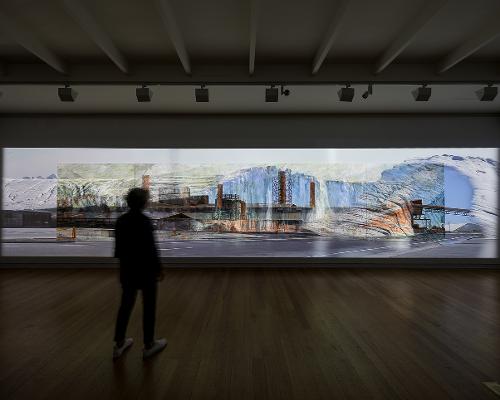
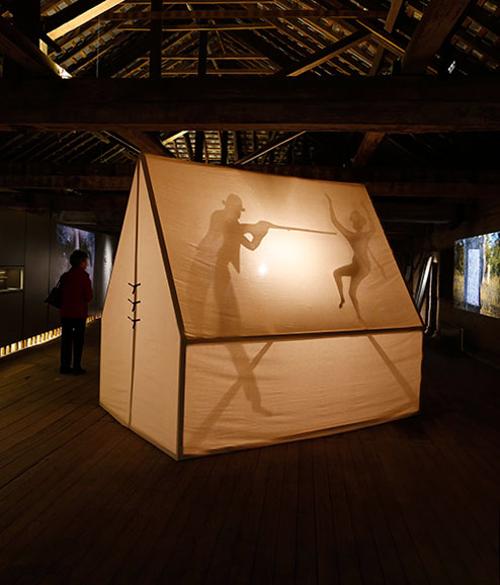
One of Tracey Moffatt’s lasting cinematographic memories, as she told me, is of films with harbour scenes, of working ports, rough workmen, the coming and going of exotic people, fogs, and foghorns. Tracey Moffatt’s photographic and film work commissioned for the Australian Pavilion in Venice responds to this landscape of cinematic time.

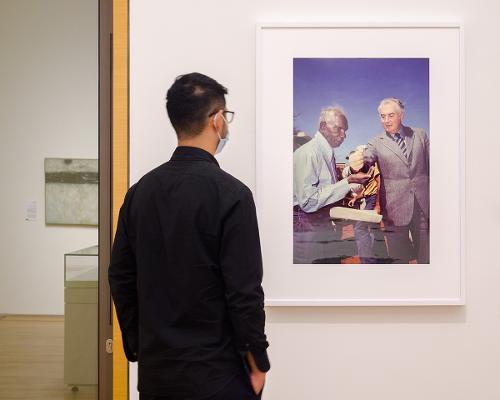
Black is the New White is Nakkiah Lui’s romantic comedy commissioned by the Sydney Theatre Company for the May/June 2017 season. It milks laughs from a stereotypical narrative of a privileged young black woman bringing her inappropriate boyfriend home to meet her parents. The twist—although not much of one these days—is that the boyfriend is white. Black is the New White is also the name of the 2007 autobiography by African American comic genius Paul Mooney. We can reach further back to the early 1990s: to Gordon Bennett’s sweet watercolours of black angels and his more ghoulish messenger between worlds, the large scarified Altered Body Print (Shadow Figure Howling at the Moon) (1994) with its mashed binaries and grotesque white/black, male/female, human/animal totemic‑like monster. Before Bennett there was Tracey Moffatt’s sweet black angel Jimmy Little on the royal telephone to heaven, an ironic serenade to her grim horror film, Night Cries (1989), which unsettled normative understandings of black/white relations with chilling effect.
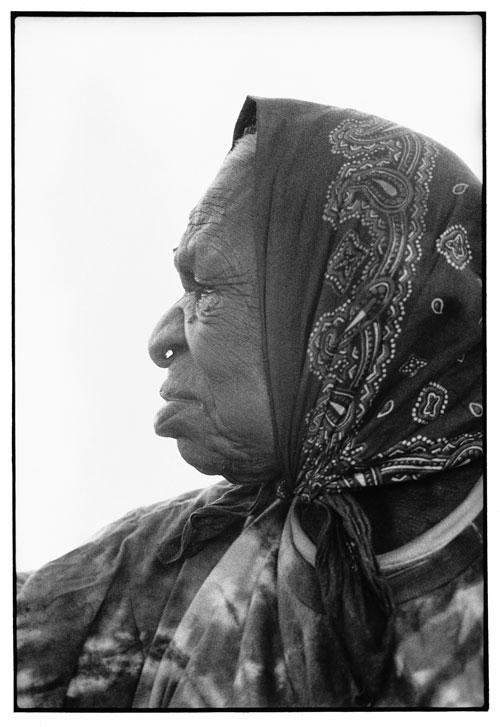

Art critic Robert Hughes made the assessment that Aboriginal art was the last great art movement of the twentieth century. It started at the Aboriginal community called Papunya, in which Aboriginal men had been painting on canvas for the outside market with great success since the 1980s. The Papunya art style, as it became known, sometimes compared to forms of Western modernism—from abstract expressionism to minimalism and even conceptual art—presented a comparison that was rarely taken literally, although some critics of the 1987 Dreamings exhibition in New York did wonder if the Aboriginal artists had been appropriating New York art. But when it came to the late paintings of Emily Kame Kngwarreye, critics really did start to question the relationship between modernism and Western Desert painting, ascribing to her the genius and expressive freedom associated with the masters of Western modernism.
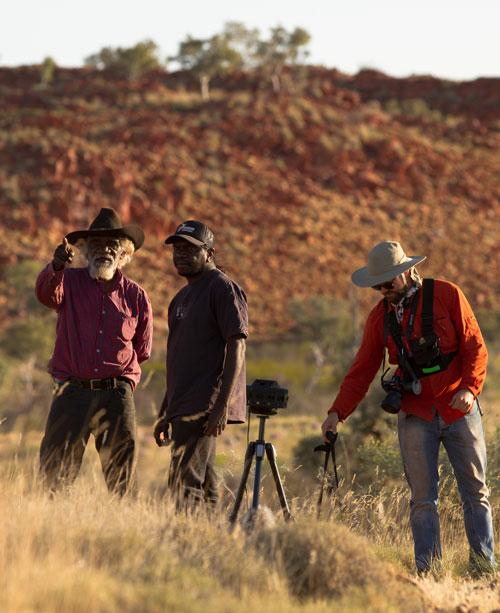

On the cross‑cultural collaborations of filmmaker Lynette Wallworth working with Nyarri Nyarri Morgan and Curtis Taylor

An emerging history of transcultural engagements in recent years is evident in the growing number of projects by Australian Indigenous artists working with collections held by British cultural institutions. From Judy Watson’s research at the British, Horniman and Science museums in the 1990s, to Daniel Boyd’s residency with the Natural History Museum and projects by Brook Andrew and Julie Gough at the Cambridge Museum of Archeology and Anthropology, these Australian Indigenous artists have negotiated complex histories of colonial collecting practices, contemporary modes of museum display, issues of cultural ownership and repatriation, as well as the role of the artist as a new kind of researcher and interpreter of archives and cultural heritage.
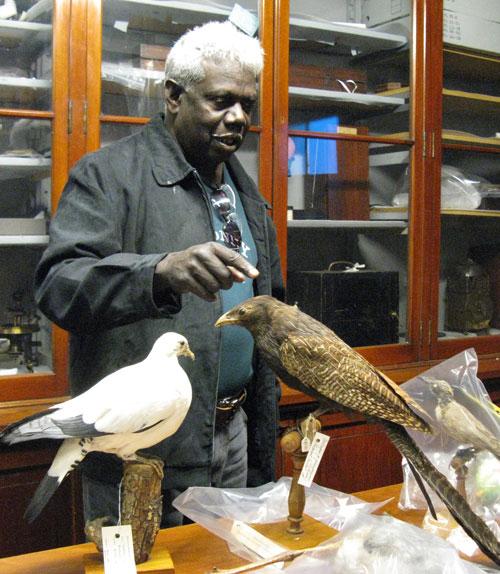

I can remember the first time I was taken into a museum storeroom. I remember it being still, organised, open and unashamed. I could see countless rows of shelving stretching from the floor to a ceiling so high that the optical illusion it created masked its vastness. The air was unmoving, the smell musty and organic. When my eyes adjusted to what lay on these shelves I had trouble taking it all in: wood, feathers, stone, bark, ochre worked in countless combinations. I searched for the clues which would guide me to material from north‑western New South Wales, to my Father’s country, and my ngurrambaa (Yuwaalaraay) or “family land”.

Keynote address presented on 17 April 2015 in Perth as part of the annual Revealed program supporting emerging Aboriginal artists from Western Australia.
As Indigenous people of this nation we are a sovereign people, standing strong in our culture and remaining true to our heritage. We stand strong in our art; we stand strong in our culture and we stand strong on our country. Our ancestors, communities and families have welcomed many non-Indigenous peoples into this country, and today we see the continuity of our shared culture, history and traditions. I see Aboriginal art and culture at the very forefront of Australian identity and celebrated in such a way that previous generations would not have imagined. Despite these remarkable achievements, we as Aboriginal people in this country have been continually bombarded by waves of dispossession, racism, marginalisation and genocide. I am both angered and frustrated that we continue to sustain the impact of colonisation on a daily basis some 226 years after invasion. We are not recognised as a sovereign people, we continue to be governed by a nation that does not recognise us as equals.
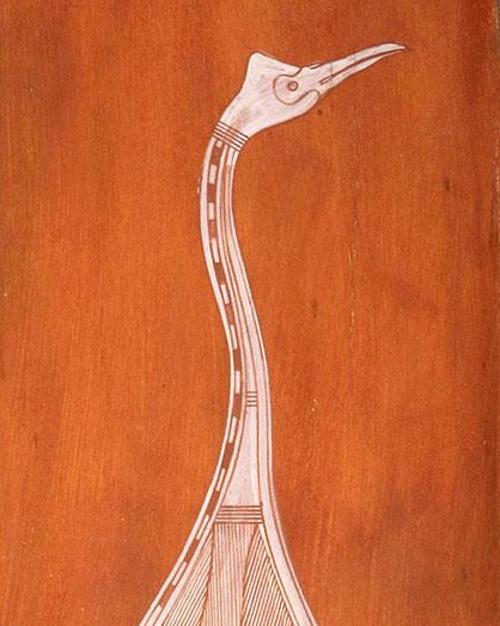
Words are like territories. Like invisible boundaries laid down in the vast forest of experience, they parcel up reality into sections which can be named, like addresses or the clan estates of Arnhem Land. To compare two languages can be like overlaying the maps of two different cultures. Just as Manilakarr clan lands, for example, are split between Kakadu National Park and Arnhem Land, the conceptual boundaries of words in two languages rarely align neatly.
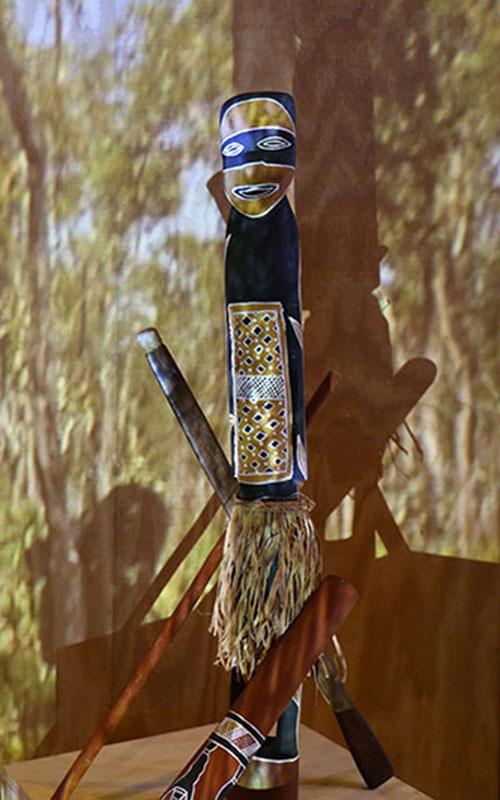

Yolngu have always had art inside our rumbal (bodies) and our doturrk (hearts). What people make depends on their aims, skill and style. With mobile phones and video cameras we’re making a new kind of Yolngu art. But it still comes from inside. It still comes from Yolngu doturrk.
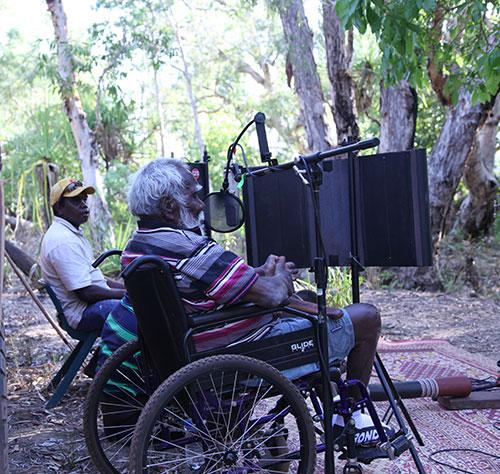

Yolngu people, the traditional Aboriginal owners of North East Arnhem Land, use the word mulka to describe a sacred, but public, ceremony. Mulka also means to protect and share things that are important to us – things that hold our identity, our culture, our connection to country and our past. When our people decided to bring together the films, photographs and audio recordings made in and about our community, the Mulka Project was born.

Beginning with batik printing at Ernabella in the APY Lands in the 1940s, hand-printed textiles in Indigenous art centres have become a rich and varied tradition. It has emerged as a significant art form in recent years, particularly for art centres in the Top End.
The Tiwi Islands has one of the longest traditions, where the Bima Wear women’s centre has been printing and designing since 1969, alongside Tiwi Design and the Pirlangimpi Women’s Centre. Tiwi textiles are known for their bright colours and bold designs, and are often worn by the local community.

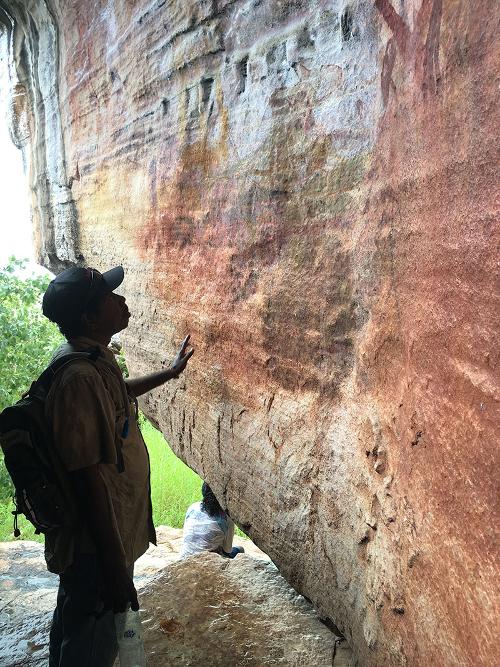
Recent changes to the Western Australian Heritage Act undermine the connection between people and country, placing thousands of rock art galleries at risk. Since the introduction of the cattle industry to the Kimberley region during the early 20th century and the subsequent forced removal of Aboriginal people from their traditional homelands, negative impacts on Aboriginal communities have been well documented. The impact on country, when its people are removed, is equally dire according to Ngarinyin/Nyikina artist, cultural leader and land management professional Rona Charles: “You can’t take people, objects, Junba [song and dance] away from Country and think nothing will happen. Because water, plant, song, animal, people – they all depend on each other. People, for their identity and social wellbeing, and country for ecology.”